springboot聚合是什么(hippo-rpcspark-rpc的增强框架)
hippo-rpc是在spark-RPC源码的基础上对流式数据传输进行了增强,用户可以更加快速的对消息或者文件进行传输。若要使用原生spark-rpc,只需改变endpointRef的ask方式,即可在hippo-rpc或spark-rpc之间进行切换。
先来看看今天的主角hippo

比较hippo和kraps(从spark分离出的RPC框架)在1KB、1MB、100MB数据上的传输时间,使用的方法如下: hippo-rpc:ask[T](message: Any, consumeResponse: (ByteBuffer) => T): Future[T] kraps-Rpc:ask[T](message: Any): Future[T]
具体ask实现方法如下:
// kraps
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.ask[String](ReadFileRequest("./testdata/inputs/1k")), Duration.Inf)
//hippo:
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.ask(ReadFileRequest("./testdata/inputs/1k"), (buf) => {
val bs = new Array[Byte](buf.remaining())
buf.get(bs)
bs
}), Duration.Inf)
每个数据量经过12次测试,传输时间结果如下,单位ms:
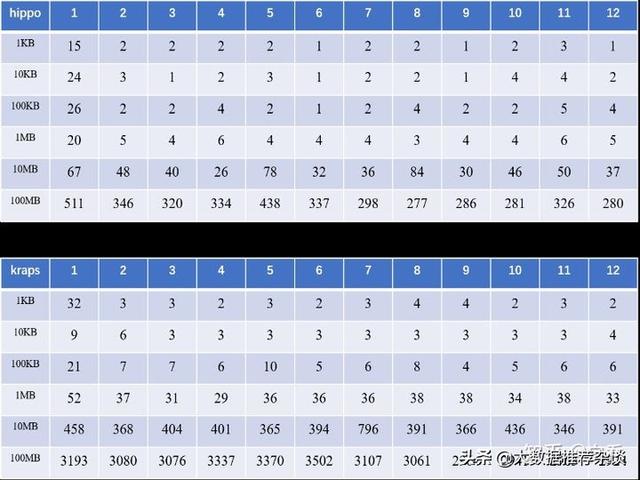
去掉最大值和最小值后,可视化1KB、1MB、100MB平均传输时间看看呢:

可见,在1KB、1MB和100MB的数据量下,hippo的加速比分别达到了52.6%、676.1%和857.9%! 再从折线图的角度去看看:

从折线图上还可以看出,在传输超过1M的文件时,hippo能够显著提高传输文件传输速度,文件越大,相比于kraps,传的越快!(如果用户想要传输更大的文件例如几个G,那就涉及到hippo的几个chunkedstream的方法了,可以先来这里看看几个stream方法的example)
还等什么,下面跟着我的步伐一起来学习一下如何使用hippo-rpc吧!
2. hippo-rpc使用说明
hippo-rpc是基于Maven的项目,用户只需在pom.xml文件的<dependencies></dependencies>中加入如下依赖即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.grapheco</groupId>
<artifactId>hippo-rpc</artifactId>
<version>0.1.2</version>
</dependency>
本部分主要从以下两个方面进行简单演示(具体细节在Client代码部分)。 1. Client发送文件到Server端(putFileTest)。 2. Client从Server端读取文件(readFileTest)。
3.1 Server端搭建第一步,和spark-rpc一样,定义一个MyEndpoint类继承RpcEndpoint,这里面receiveAndReply方法将处理Client发出的调用原生spark-rpc的消息。 其次还需要建立一个继承自HippoRpcHandler的MyStreamHandler类,这里面将处理Client调用hippo-rpc的消息。 HipporpcHandler中一共有3个方法可以根据需要进行重写: - receiveWithBuffer:处理buffer类型的消息请求 - openCompleteStream:根据请求消息返回一个数据流 - openChunkedStream:根据请求消息返回一个分块的数据流 这里以receiveWithBuffer作为例子进行展示,更多内容请访问:hippo-rpc example
class MyEndpoint(override val rpcEnv: HippoRpcEnv) extends RpcEndpoint {
override def onStart(): Unit = {
println("server started...")
}
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case SayHelloRequest(msg) => context.reply(SayHelloResponse(s"$msg response"))
}
}
class MyStreamHandler() extends HippoRpcHandler {
override def receiveWithBuffer(extraInput: ByteBuffer, context: ReceiveContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case SayHelloRequest(msg) =>
context.reply(SayHelloResponse(msg.toUpperCase()))
case PutFileRequest(totalLength) =>{
context.reply(PutFileResponse(extraInput.remaining()))
}
case ReadFileRequest(path) => {
val buf = Unpooled.buffer()
val fis = new FileInputStream(new File(path))
buf.writeBytes(fis.getChannel, new File(path).length().toInt)
context.replyBuffer(buf)
}
}
}
case class SayHelloRequest(msg: String)
case class SayHelloResponse(value: Any)
case class PutFileRequest(totalLength:Int)
case class PutFileResponse(written:Int)
case class ReadFileRequest(path: String)
第二步,将MyEndpoint和MyStreamHandler交给hippo rpc管理生命周期。 通过RpcEnvServerConfig可以定义一些参数、server名称(仅仅是一个标识)、bind地址和端口。 通过HippoRpcEnvFactory这个工厂方法,生成rpcEnv。 通过setupEndpoint将"server"这个名字和第一步定义的endpoint绑定,后续client调用路由到这个endpoint就需要"server"这个名字。 通过setRpcHandler和第一步定义的MyStreamHandler绑定。 最后调用awaitTermination来阻塞服务端监听请求并且处理。
import java.io.{File, FileInputStream}
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled
import net.neoremind.kraps.RpcConf
import net.neoremind.kraps.rpc.{RpcAddress, RpcEnvClientConfig}
import net.neoremind.kraps.rpc.netty.{HippoEndpointRef, HippoRpcEnvFactory}
import scala.concurrent.Await
import scala.concurrent.duration.Duration
object HippoServer {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val config = RpcEnvServerConfig(new RpcConf(), "server", "localhost", 12345)
val rpcEnv = HippoRpcEnvFactory.create(config)
val endpoint = new MyEndpoint(rpcEnv)
val handler = new MyStreamHandler()
rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("server", endpoint)
rpcEnv.setRpcHandler(handler)
rpcEnv.awaitTermination()
}
}
Client部分比较简单,通过RpcEnvClientConfig设置参数,通过HippoRpcEnvFactory创建rpcEnv,在setupEndpointRef时,参数要设置为server的端口地址和server端绑定的endpoint的名字。之后便可以通过endpointRef发送RPC请求。
import java.io.{File, FileInputStream}
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled
import net.neoremind.kraps.RpcConf
import net.neoremind.kraps.rpc.{RpcAddress, RpcEnvClientConfig}
import net.neoremind.kraps.rpc.netty.{HippoEndpointRef, HippoRpcEnvFactory}
import scala.concurrent.Await
import scala.concurrent.duration.Duration
object HippoClient {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val config =RpcEnvClientConfig(new RpcConf(), "client")
val rpcEnv = HippoRpcEnvFactory.create(config)
val endpointRef = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(new RpcAddress("localhost", 12345), "server")
val res = sayHelloHippoRpcTest(endpointRef)
println(res)
rpcEnv.shutdown()
}
def sayHelloSparkRpcTest(endpointRef:HippoEndpointRef): Any ={
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.ask[SayHelloResponse](SayHelloRequest("hello")), Duration.Inf)
res.value
}
def sayHelloHippoRpcTest(endpointRef:HippoEndpointRef): Any ={
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.askWithBuffer[SayHelloResponse](SayHelloRequest("hello")),Duration.Inf)
res.value
}
def putFileTest(endpointRef:HippoEndpointRef): Int ={
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.askWithBuffer[PutFileResponse](PutFileRequest(new File("./testdata/input/1k").length().toInt), {
val buf = Unpooled.buffer(1024)
val fos = new FileInputStream(new File("./testdata/input/1k"));
buf.writeBytes(fos.getChannel, new File("./testdata/input/1k").length().toInt)
fos.close()
buf
}), Duration.Inf)
res.written
}
def readFileTest(endpointRef:HippoEndpointRef): String ={
val res = Await.result(endpointRef.ask(ReadFileRequest("./testdata/input/1k"), (buf)=>{
val bs = new Array[Byte](buf.remaining())
buf.get(bs)
bs
}), Duration.Inf)
val fileContent = new String(res)
fileContent
}
}
endpointRef有如下几种发起RPC请求的方式: 1. ask[T](message: Any): Future[T] 2. ask[T](message: Any, timeout: RpcTimeout): Future[T] 3. ask[T](message: Any, timeout: Duration): Future[T] 4. send(message: Any): Unit 注:以上四种方式将通过spark-rpc的方式进行消息传递,在Server端MyEndpoint的receiveAndReply方法中进行处理。如Client代码中sayHelloSparkRpcTest方法。
以下方法为hippo-rpc方法,在Server端MyStreamHandler类中进行消息处理,其中5和6在receiveWithBuffer方法中处理;7在openCompleteStream方法中处理;8和9在openChunkedStream方法中处理。 5. ask[T](message: Any, consumeResponse: (ByteBuffer) => T): Future[T]:使用consumeResponse来解析响应的消息,可以使用来读取Server端的文件,如Client代码的readFileTest方法。 6. askWithBuffer[T](message: Any, extra: ByteBuf*): Future[T]:发送消息或者文件到Server端,如Client代码的sayHelloHippoRpcTest和putFileTest方法。 7. getInputStream(request: Any, waitStreamTimeout: Duration): InputStream:将Server端指定文件通过stream方式全部读到Client端后在本地组成一个inputStream。 8. getChunkedInputStream(request: Any, waitStreamTimeout: Duration): InputStream:通过分块的方式将Server端指定文件读到本地组成一个inputStream。 9. getChunkedStream[T](request: Any, waitStreamTimeout: Duration): Stream[T]:通过分块的方式将stream数据读到本地,该stream以行为单位。
,免责声明:本文仅代表文章作者的个人观点,与本站无关。其原创性、真实性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容文字的真实性、完整性和原创性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并自行核实相关内容。文章投诉邮箱:anhduc.ph@yahoo.com






