简单的pytorch语句(Pytorch中的四种经典Loss源码解析)
笔者最近在OneFlow框架对齐实现Pytorch相关Loss代码,其中也涉及到部分源码解读,数学特殊操作等知识,于是想写篇文章简单总结一下。
关于Pytorch的Loss源码了解过Pytorch的应该知道其历史包袱比较重,它吸收了Caffe2的底层代码,然后自己借用这部分底层代码来写各种OP的逻辑,最后再暴露出一层Python接口供用户使用。
因此第一次接触Pytorch源代码可能有点不太熟悉,基本上Pytorch大部分OP逻辑实现代码都放在 Aten/native下,我们这里主要是根据Loss.cpp来进行讲解
MarginRankingLossRankingLoss系列是来计算输入样本的距离,而不像MSELoss这种直接进行回归。其主要思想就是分为 Margin 和 Ranking 。
MarginRankingLoss公式
Margin 这个词是页边空白的意思,平常我们打印的时候,文本内容外面的空白就叫 Margin。
而在Loss中也是表达类似的意思,相当于是一个固定的 范围 , 当样本距离(即Loss)超过范围,即表示样本差异性足够了 ,不需要再计算Loss。
Ranking 则是排序,当target=1,则说明x1排名需要大于x2;当target=2,则说明x2排名需要大于x1。其源码逻辑也很简单,就是根据公式进行计算,最后根据reduction类型来进行 reduce_mean/sum
Pytorch的MarginRankingLoss代码
下面是对应的numpy实现代码
def np_margin_ranking_loss(input1, input2, target, margin, reduction):
output = np.maximum(0, -target*(input1 - input2) margin)
if reduction == "mean":
return np.mean(output)
elif reduction == "sum":
return np.sum(output)
else:
return output
TripletLoss最早是在 FaceNet 提出的,它是用于衡量不同人脸特征之间的距离,进而实现人脸识别和聚类

TripletLoss
而TripletMarginLoss则是结合了TripletLoss和MarginRankingLoss的思想,具体可参考 Learning local feature descriptors with triplets and shallow convolutional neural networks其公式如下
TripletMarginLoss公式
其中d是p范数函数
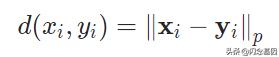
距离函数
范数的具体公式是

范数公式
该Loss针对不同样本配对,有以下三种情况
- 简单样本,即
此时 正样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, pi) Margin 仍然小于 负样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, ni) ,该情况认为正样本距离足够小,不需要进行优化,因此Loss为0
- 难样本,即
此时 负样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, ni) 小于 正样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, pi) ,需要优化
- 半难样本,即
此时虽然 负样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, ni) 大于 正样本距离anchor的距离d(ai, pi) ,但是还不够大,没有超过 Margin,需要优化

此外论文作者还提出了 swap 这个概念,原因是我们公式里 只考虑了anchor距离正类和负类的距离 ,而 没有考虑正类和负类之间的距离 ,考虑以下情况

可能Anchor距离正样本和负样本的距离相同,但是负样本和正样本的距离很近,不利于模型区分,因此会做一个swap,即交换操作,在代码里体现的操作是取最小值。
## 伪代码
if swap:
D(a, n) = min(D(a,n), D(p, n))
这样取了最小值后,在Loss计算公式中,Loss值会增大,进一步帮助区分负样本。
有了前面的铺垫,我们理解Pytorch的TripletMarginRankingLoss源码也非常简单

TripletMarginLoss源码
at::pairwise_distance 是距离计算函数,首先计算出了anchor与正类和负类的距离。 然后根据参数 swap ,来确定是否考虑正类和负类之间的距离。最后 output 就是按照公式进行计算,下面是numpy的对应代码
def np_triplet_margin_loss(anchor, postive, negative, margin, swap, reduction="mean", p=2, eps=1e-6):
def _np_distance(input1, input2, p, eps):
# Compute the distance (p-norm)
np_pnorm = np.power(np.abs((input1 - input2 eps)), p)
np_pnorm = np.power(np.sum(np_pnorm, axis=-1), 1.0 / p)
return np_pnorm
dist_pos = _np_distance(anchor, postive, p, eps)
dist_neg = _np_distance(anchor, negative, p, eps)
if swap:
dist_swap = _np_distance(postive, negative, p, eps)
dist_neg = np.minimum(dist_neg, dist_swap)
output = np.maximum(margin dist_pos - dist_neg, 0)
if reduction == "mean":
return np.mean(output)
elif reduction == "sum":
return np.sum(output)
else:
return output
这里比较 容易踩坑的是p范数的计算 ,因为当p=2,根据范数的公式, 如果输入有负数是不合法的 , 比如
于是我们从distance函数开始找线索,发现它是调用 at::norm
pairwise_distance
根据Pytorch的文档,它其实在 计算的时候调用了abs绝对值 ,来避免最后负数出现,从而保证运算的合理性

Norm文档
KLDivLoss该损失函数是计算KL散度(即相对熵),它可以用于衡量两个分布的差异

KL散度基本定义
当p和q分布越接近,则趋近于1,经过log运算后,loss值为0
当分布差异比较大,则损失值就比较高
Pytorch中计算公式中还不太一样
Pytorch的KLDivLoss公式
下面我们看看Pytorch对应的源码

KLDivLoss源码
首先可以观察到,除了常规的input,target,reduction,还有一个额外的参数 log_target ,用于表示target是否已经经过log运算。根 据这个参数,KLDivLoss进而分成两个函数 _kl_div_log_target 和 _kl_div_non_log_target 实现。
_kl_div_log_target 的实现比较简单,就是按照公式进行计算
而 _kl_div_non_log_target 有些许不同,因为target的数值范围不确定, 当为负数的时候,log运算时不合法的 。因此Pytorch初始化了一个全0数组,然后在最后的loss计算中, 在target小于0的地方填0,避免nan数值出现
下面是对应的numpy实现代码
def np_kldivloss(input, target, log_target, reduction="mean"):
if log_target:
output = np.exp(target)*(target - input)
else:
output_pos = target*(np.log(target) - input)
zeros = np.zeros_like(input)
output = np.where(target>0, output_pos, zeros)
if reduction == "mean":
return np.mean(output)
elif reduction == "sum":
return np.sum(output)
else:
return output
熟悉二分类交叉熵损失函数BCELoss的应该知道,该函数输入的是个分类概率,范围在0~1之间,最后计算交叉熵。我们先看下该损失函数的参数

BCEWithLogitsLoss参数
- weight 表示最后loss缩放权重
- mean sum none
- pos_weight 表示针对正样本的权重,即positive weight
下面是其计算公式 其中表示sigmoid运算
BCEWithLogitsLoss
BCEWithLogitsLoss 相当于 sigmoid BCELoss,但实际上 Pytorch为了更好的数值稳定性,并不是这么做的,下面我们看看对应的源代码

Pytorch的BCEWithLogitsLoss源码
这段源代码其实看的不太直观,我们可以看下numpy对应的代码
def np_bce_with_logits_loss(np_input, np_target, np_weight, np_pos_weight, reduction="mean"):
max_val = np.maximum(-np_input, 0)
if np_pos_weight.any():
log_weight = ((np_pos_weight - 1) * np_target) 1
loss = (1 - np_target) * np_input
loss_1 = np.log(np.exp(-max_val) np.exp(-np_input - max_val)) max_val
loss = log_weight * loss_1
else:
loss = (1 - np_target) * np_input
loss = max_val
loss = np.log(np.exp(-max_val) np.exp(-np_input - max_val))
output = loss * np_weight
if reduction == "mean":
return np.mean(output)
elif reduction == "sum":
return np.sum(output)
else:
return output
因为涉及到了sigmoid运算,所以有以下公式
计算中,如果x过大或过小,会 导致指数运算出现上溢或下溢 ,因此我们可以 用 log-sum-exp 的技巧来 避免数值溢出 ,具体可以看下面公式推导( 特此感谢德澎! )

公式推导
总结看源代码没有想象中那么难,只要破除迷信,敢于尝试,你也能揭开源码的神秘面纱~
相关链接- triplet-loss(https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss)
- FaceNet(https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.03832.pdf)
- TripletMarginLoss(http://www.bmva.org/bmvc/2016/papers/paper119/paper119.pdf)
- RankingLoss(https://gombru.github.io/2019/04/03/ranking_loss/)
免责声明:本文仅代表文章作者的个人观点,与本站无关。其原创性、真实性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容文字的真实性、完整性和原创性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并自行核实相关内容。文章投诉邮箱:anhduc.ph@yahoo.com






